Electric hoists are widely used in industrial material handling, significantly improving cargo transfer efficiency. However, they can be prone to malfunction due to long-term use, improper operation, or environmental factors. Promptly troubleshooting and resolving issues is crucial to ensuring safe operation and maintaining smooth production processes. This article details seven common electric hoist malfunctions and provides basic electric hoist maintenance tips.
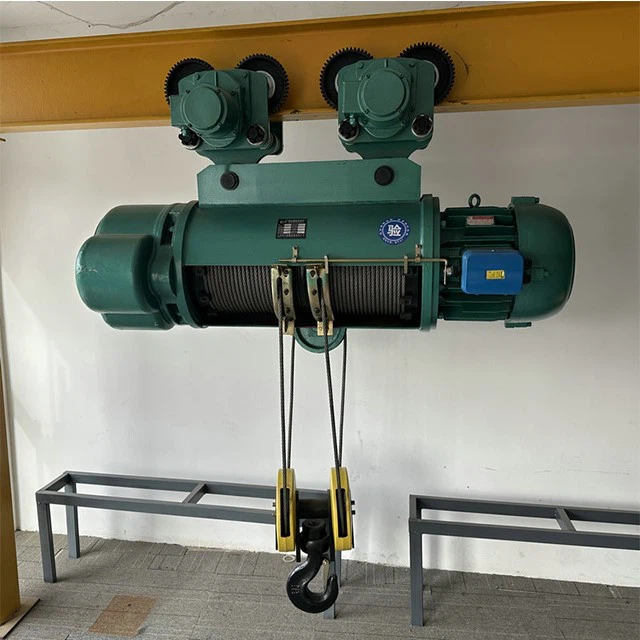
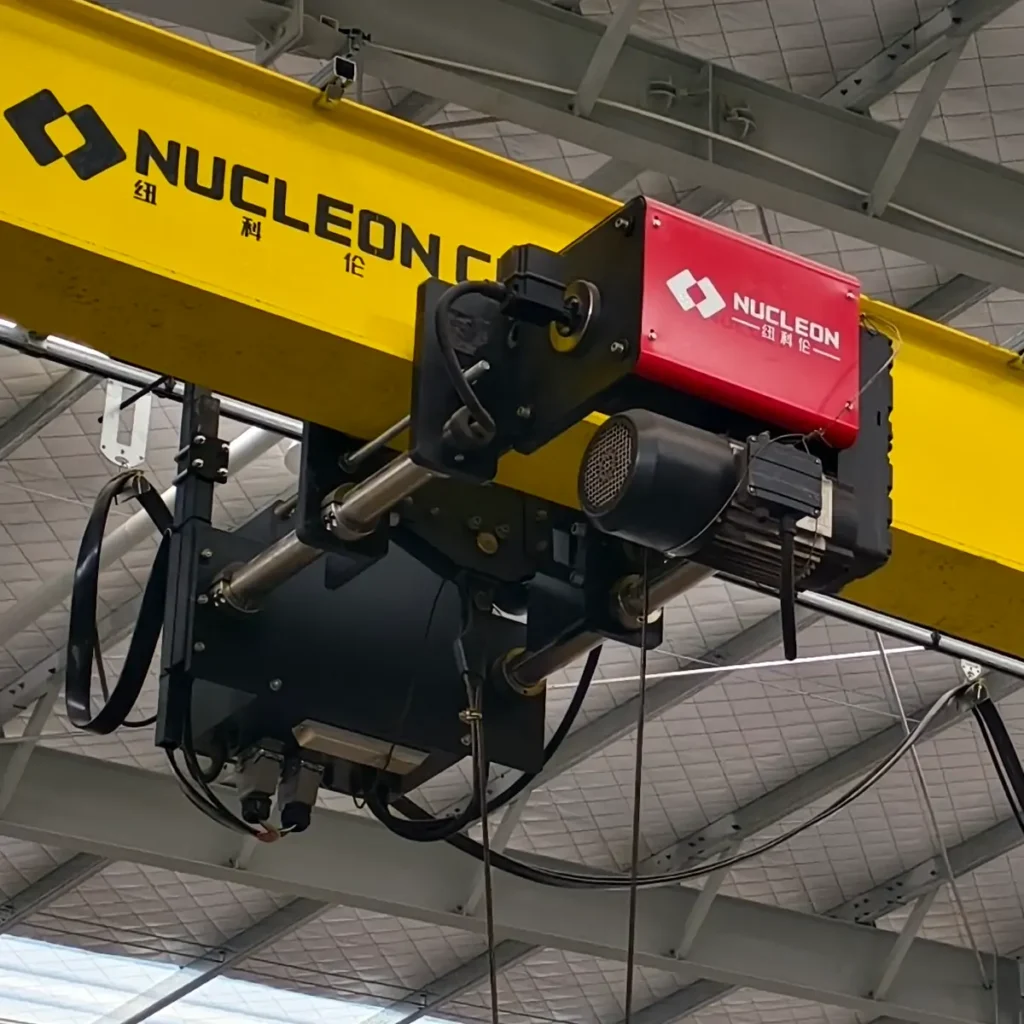



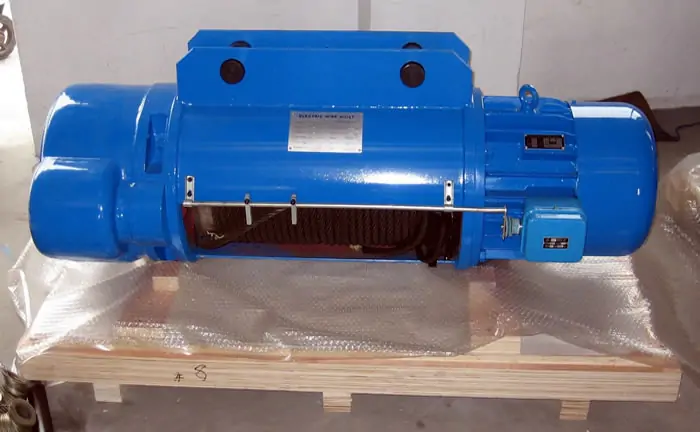
Abnormal noise occurs during equipment operation
Problems
Abnormal noise from equipment is a common fault, typically occurring in the motor or gearbox.
- It may be because the motor is running in single-phase or the bearing is damaged. If a sharp and harsh sound occurs, it may be because the rotor is misaligned or parts are scraping against each other.
- A grinding or rumbling noise can be caused by worn transmission gears, bearings, or the transmission housing, or even by insufficient or deteriorating lubricant.
Solution
- If the motor makes an unusual noise, stop the hoist immediately to avoid damaging the circuit and worsening the problem. Check and correct the power phase connection, inspect the motor bearings and replace worn parts, recalibrate the stator and rotor position, or replace worn support rings. For a critical component like the motor, consult a professional immediately if necessary.
- If the gearbox makes unusual noises, first check the gears and bearings for cracks, deformation, or excessive wear. If so, replace the damaged parts immediately. Then, refill the lubricant and replace it with new oil to ensure quality.

The electric hoist does not respond to the remote control or pendant controller
Problems
This type of problem is mostly caused by power supply problems or circuit failures.
- Regarding power supply, there may be a power outage. For example, the main power switch is not turned on, the fuse is blown, the circuit breaker is tripped, or the power cord is loose or disconnected. It may also be due to low voltage or frequency mismatch.
- In terms of circuits, there may be loose connections in the internal wiring, control panel, or pendant cables, or the wires may be burned or damaged. It may also be a contactor failure, which may manifest as normal manual operation but no electrical response.
Solution
- For power supply problems: If the power supply is interrupted, check the main power switch, fuses, and circuit breakers, and replace burnt fuses or reset circuit breakers. Use a voltmeter to measure the power supply voltage and stabilize the abnormal voltage within the rated range. At the same time, ensure that the current on-site is consistent with the hoist specifications.
- For circuit problems: check the circuit, panel, and cable against the hoist wiring diagram, repair or replace the faulty part, unlock the activated emergency stop switch, and replace the damaged pendant button.If the contactor fails and the manual and electric controls are normal but there is no response, check and replace the contactor coil or control circuit as needed. If both the manual and electric controls fail and the power supply is normal, replace the contactor directly.

The hoist cannot stop or slide after stopping
Problems
This problem poses a serious safety hazard and may cause overtravel or load slippage, mostly due to damage to the braking system or limit switch.
- If the hoist continues to run after the stop button is pressed, it may be because the contactor contacts are stuck and the stop contacts cannot be disconnected, causing the motor to continue running.
- If the hoist slips after stopping, the possible causes include brake pad wear, loose brake nut, weakened brake spring force, and motor coupling failure that causes the brake disc and end cover to not fit properly.
Solution
- If the machine continues to run after pressing the stop button, you must immediately cut off the main power supply to prevent accidents, disassemble the contactor, and check the contacts. If the contactor cannot be repaired, it must be replaced in time.
- The equipment slides after stopping. Refer to the electric hoist manual to adjust the brake nut and replace any worn brake pads or springs. Use a non-flammable cleaner to clean the brake friction surface from oil and dust. Also, check the motor coupling and repair or replace it if it's stuck or misaligned.

The hoist is running in the wrong direction
Fault
This type of problem is often caused by incorrect wiring or phase sequence.
- One is that the power phase sequence is wrong.
- The second is that the wiring at the control station, terminal board, or motor leads is reversed.
- The third is that the motor reversing switch of the single-phase hoist fails, which may be accompanied by capacitor damage.
Solution
- If the power phase sequence is incorrect, use a phase detector to check the three-phase power supply and swap the positions of the two phase wires to correct the sequence.
- If the wiring is reversed, check the relevant wiring according to the hoist wiring diagram and reconnect the reverse wires.
- If the single-phase hoist reversing switch fails, it is necessary to focus on checking the switch capacitor.

Motor overheating
Fault
Motor overheating shortens the hoist's lifespan and may trigger a thermal shutdown.
- Motor overheating is often caused by overloading, but worn or damaged bearings can also contribute to overheating.
- If the brake gap is too small, friction increases, leading to overheating and motor damage.
Solution
- If overheating occurs due to overloading, ensure that the load does not exceed the rated lifting capacity and reduce the load to within the limit.
- Clean the dirt on the bearings in time and replace the bearings if necessary.
- If the brake clearance is too small , the crane should be stopped immediately, and the brake clearance should be readjusted after a thorough inspection.
Transmission oil leakage
Fault
This condition can reduce the lubrication of the gear train and even damage internal components . Common causes include aging and wear of the seal ring , or loose gearbox bolts causing a gap between the housing and the end cover.
Solution
- If the seal is worn or damaged, stop the hoist, disassemble the gearbox cover, and replace it with a new seal of the same specification.
- If the bolts are loose, tighten them evenly according to the instructions to eliminate the gap between the shell and the end cover.
Wire rope-specific problems
Fault
wire rope electric hoist occurs on the wire rope.
- The wire rope frequently carries heavy loads and rubs against pulleys and drums, resulting in broken wires, exposed rope cores or indentations.
- Wire rope misalignment is generally caused by improper calibration of the drum and pulley, or irregular diagonal pulling operations resulting in uneven winding.
- Wire ropes are exposed to moisture, chemicals or other harsh environments, causing corrosion.
- Improper installation of the wire rope or loss of tension during use may cause the wire rope on the drum to become loose and weak as a whole.
Solution
- Check the wire rope regularly and replace it in time if the wear exceeds the specified limit .
- If misaligned, realign the drum and pulley to ensure even winding, avoid slanting, and ensure the load is directly under the hoist.
- If rust occurs, clean the wire rope with a wire brush and apply anti-rust lubricant . If rust is severe, replace it.
- If it is loose, adjust the tension according to the instructions. If it is loosely wound, reinstall the wire rope.
Conclusion
The operation of electric hoists is directly related to production efficiency and operational safety. This article only summarizes the inspection and maintenance methods for some common faults. Daily standard operation, regular inspections, and timely lubrication and maintenance are key to reducing the frequency of faults and extending equipment life. If you encounter a complex fault during actual operation or have any questions about the fault diagnosis, do not blindly dismantle the hoist for repair. You should immediately contact a professional technical team for repair.