Rubber-tyred gantry cranes (RTGs) and rail-mounted gantry cranes (RMG) are core equipment in modern port container terminals, railway freight yards, and logistics hubs, responsible for the efficient stacking, transshipment, and loading/unloading of containers. Although their functions are similar, they differ significantly in terms of structure, operating principles, application scope, advantages and disadvantages, and economic costs. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the key differences between RTG vs RMG cranes, helping you select the optimal solution based on your specific requirements.
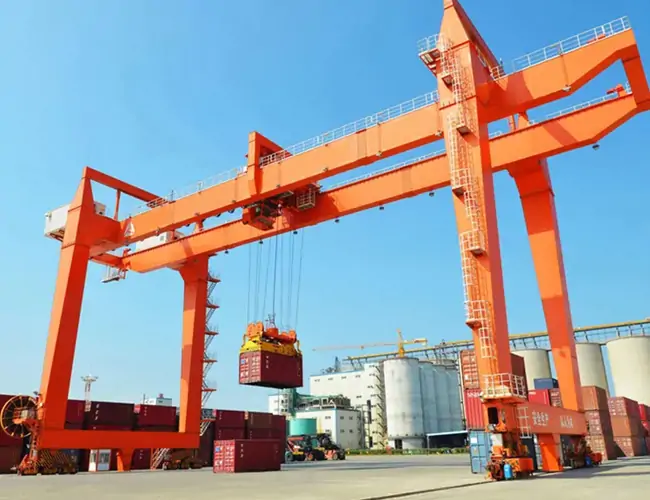
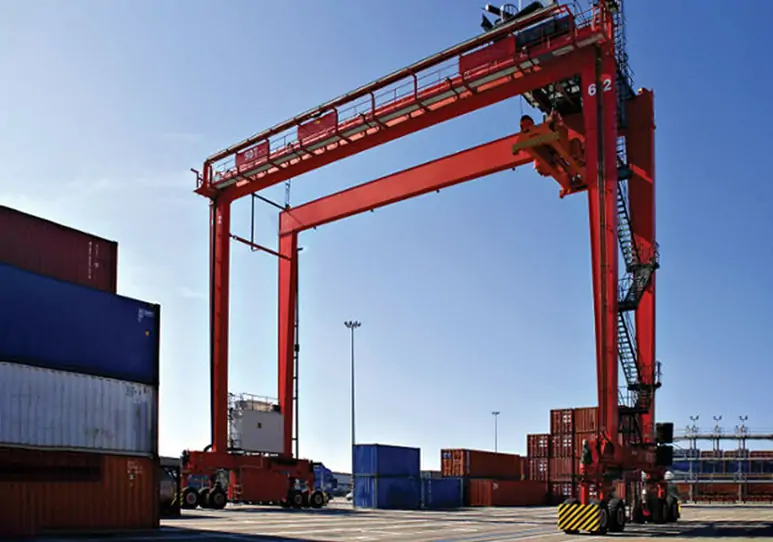


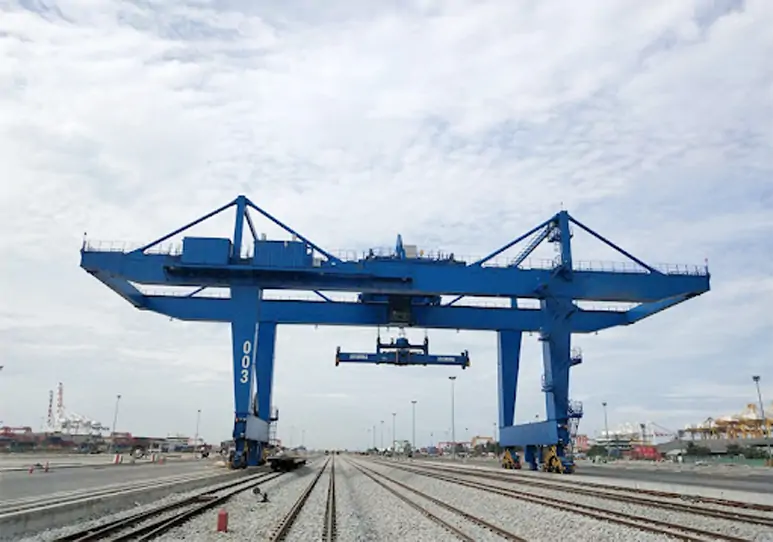
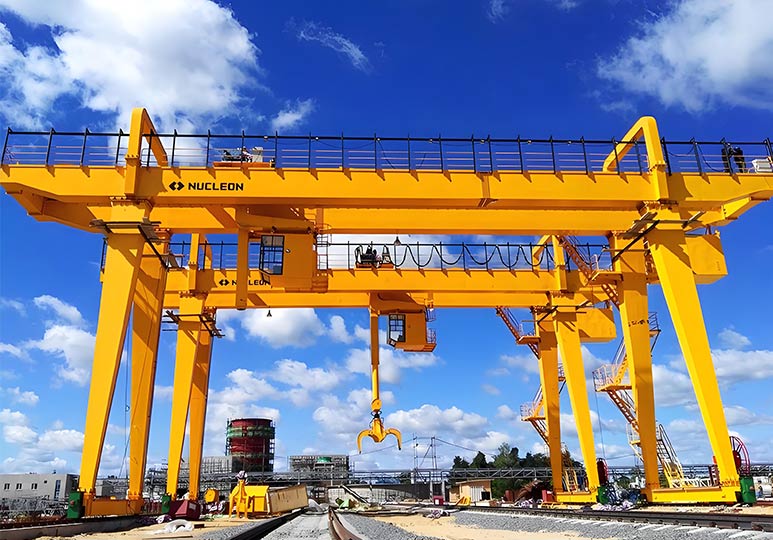
What are RTG and RMG Cranes?
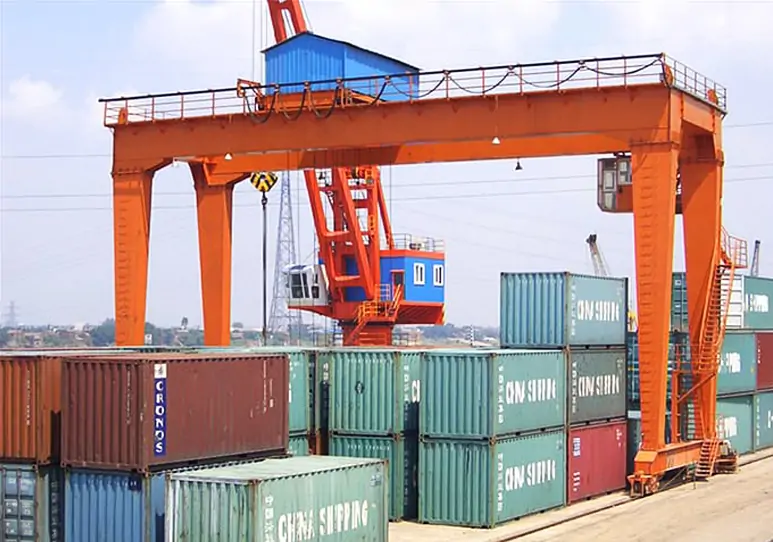
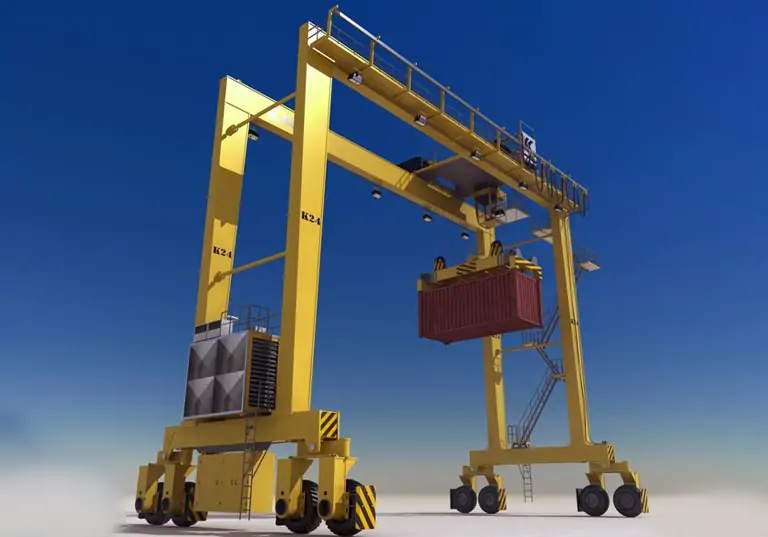
RTG (Rubber-Tired Gantry Crane)
RTG (Rubber-Tired Gantry Crane) uses a rubber tire travel system, enabling it to move freely within the yard and is suitable for flexible loading and unloading operations. Its features include high mobility, suitability for multi-row container stacking, and the ability to adapt to different work areas through relocation. If you want to learn more, please click this article: What Is An RMG Crane? Comprehensive Guide
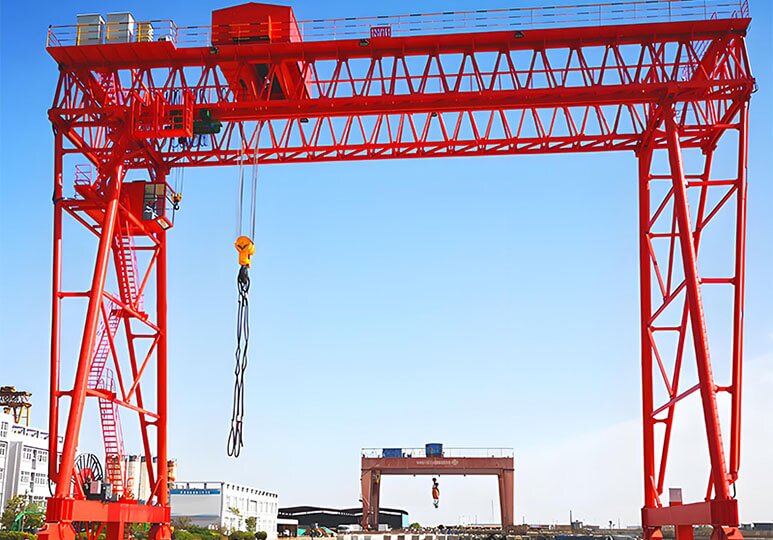
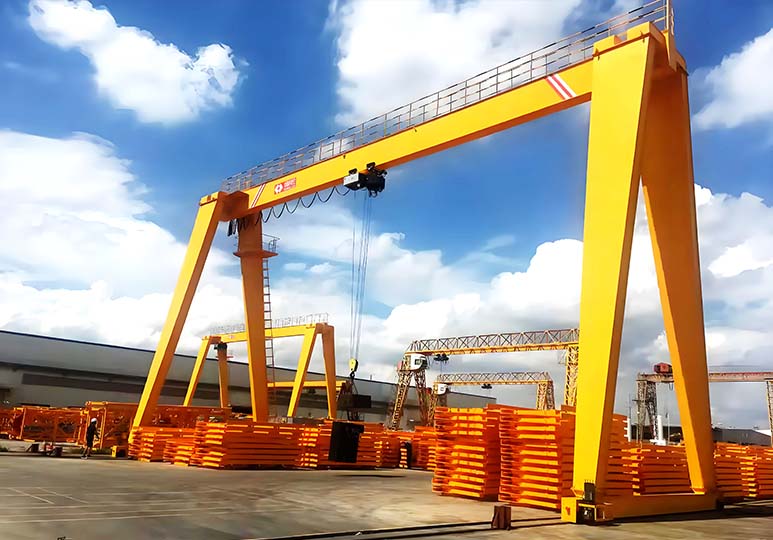
RMG (Rail-Mounted Gantry Crane)
RMG (Rail-Mounted Gantry Crane) operates along fixed tracks, offering stable structure and suitability for high-density, automated container yards. Its advantages include high-precision positioning and low energy consumption, making it particularly suitable for long-term fixed-operation scenarios.
RTG vs RMG Cranes: Structural Differences
Both RTG and RMG cranes consist of a steel structure frame, hoisting mechanism, main crane running mechanism, trolley running mechanism, electrical system, and safety devices. The key differences are as follows:
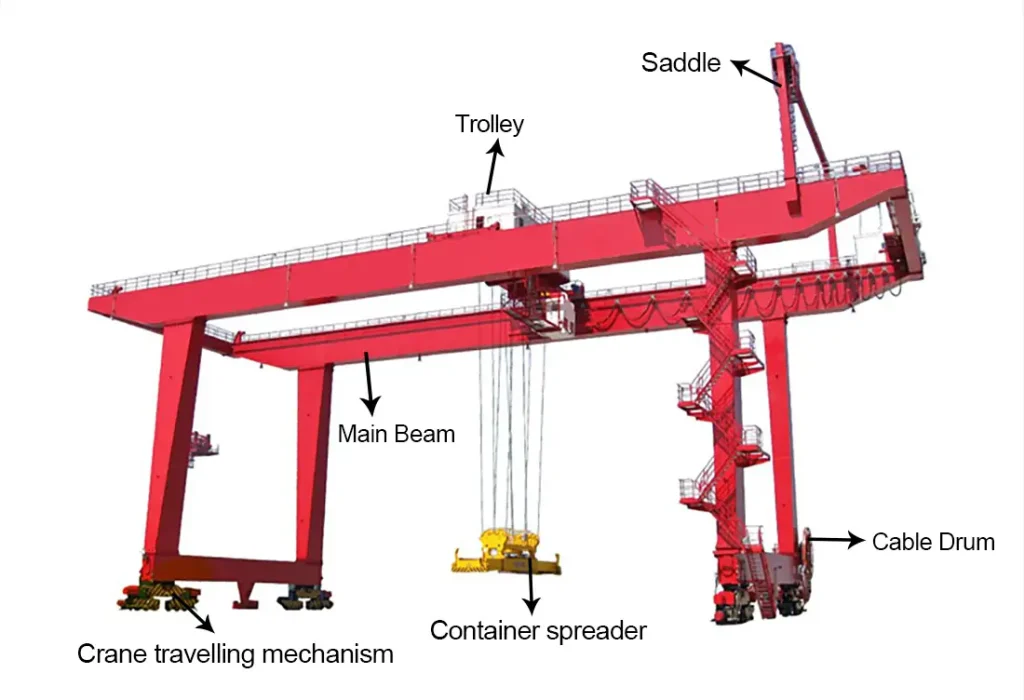
RTG crane: Uses rubber tires + diesel/electric drive, offering greater structural flexibility but requiring strong ground bearing capacity.
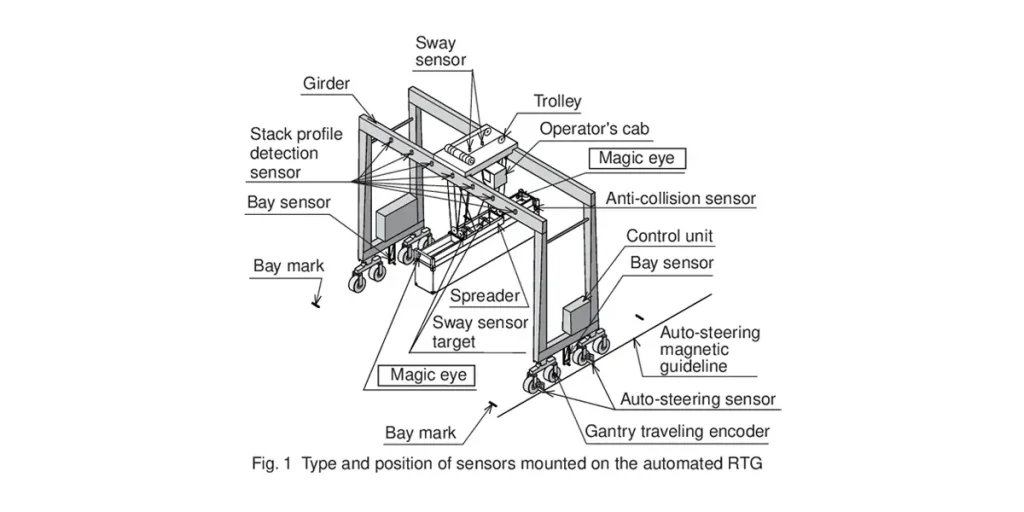
RMG crane: Operates on fixed tracks, offering greater structural stability and suitability for long-term high-intensity operations, but with limited mobility.
RTG vs RMG Cranes: Different Working Principles
RTG Cranes: Move freely on tires, can operate across container yards, but are greatly affected by ground flatness. They are usually powered by diesel generators or mains electricity.
RMG Cranes: Run along tracks, have high positioning accuracy, are suitable for automated control, and are usually powered by sliding contact lines, resulting in lower energy consumption.
Specifications Comparison
| Key Parameters | RTG Crane | RMG Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Service Life | 15 years | 25 years |
| Basic Depreciation Rate | 6.80% | 4% |
| Major Repair Cost Ratio | 2.50% | 1.50% |
| Daily Maintenance Cost Ratio | 0.70% | 0.10% |
| Capacidade nominal de elevação | 40.5 tons | 40.5 tons |
| Span Characteristics | Small span, no cantilever design | Large span, can be configured with cantilever |
| Altura de elevação | 5-tier stacking/6-tier cross-transport | 5-layer stacking/6-layer cross transport |
| Base Distance Dimensions | Smaller | Larger |
| Full Load Lifting Speed | Slower | Faster |
| No Load Lifting Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Velocidade de deslocação do trólei | Slower | Faster |
| Drive Mode | Diesel-electric (mainstream) or diesel-hydraulic (less common) | AC variable frequency drive or thyristor DC drive |
| Travel Mechanism | 8 pneumatic tires, good maneuverability, supports diagonal or four-wheel drive | 16-24 steel wheels, fixed track operation, cannot turn |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher (diesel-driven) | Lower (electric drive) |
| Automation Compatibility | Requires upgrade (ERTG) | Native support for full automation (ARMG) |
Uses of RTG and RMG Cranes:
RTG cranes are commonly used in container terminals that require frequent relocation, logistics centers with limited yard space but flexible adjustment needs, and intermodal (road + rail) transfer stations.




RMG cranes are commonly used in automated container terminals with high-density storage, railway yards with long-term fixed operations, and logistics hubs that require high-precision stacking.
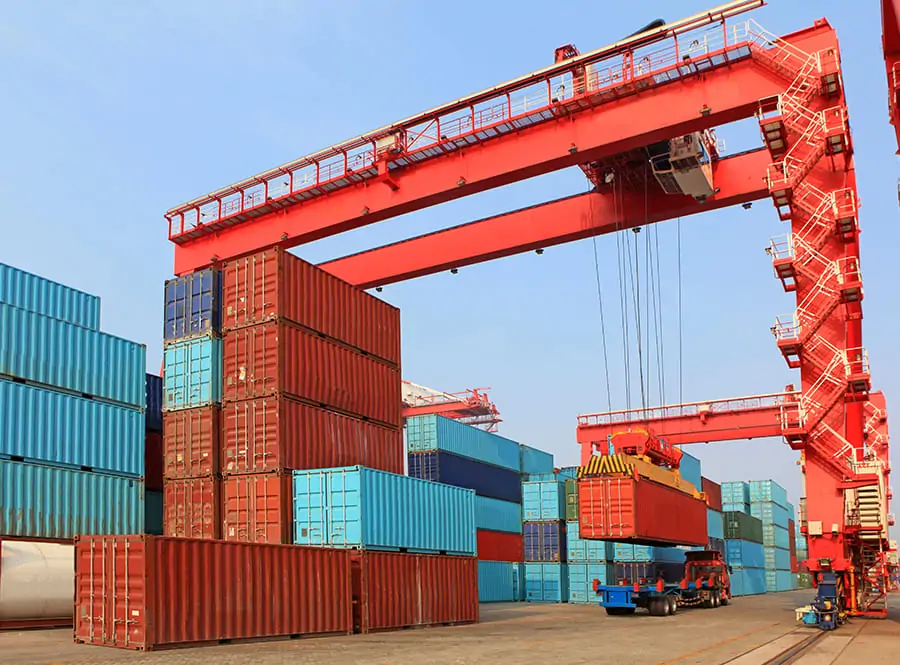
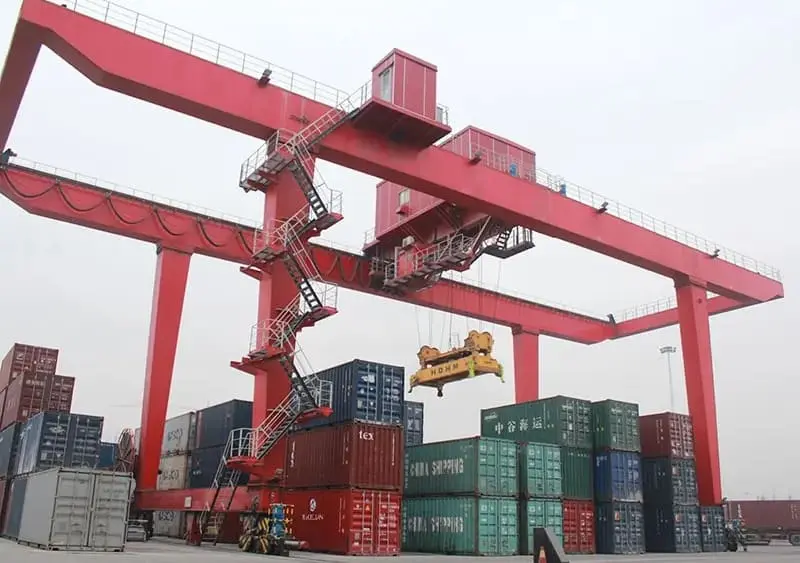
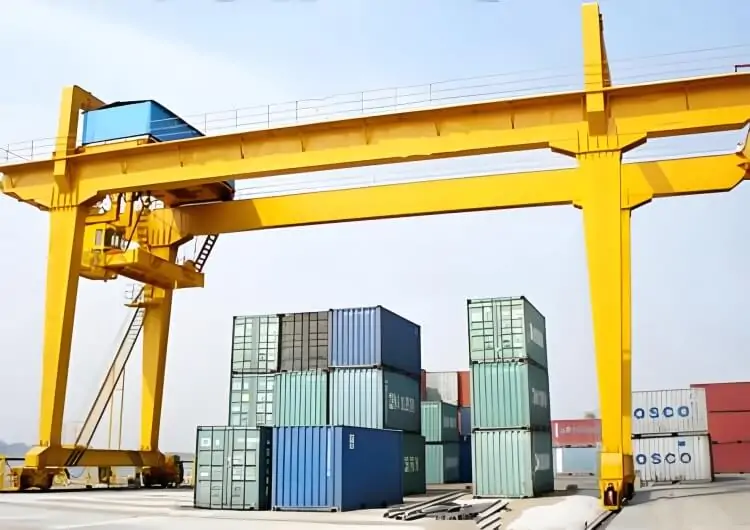
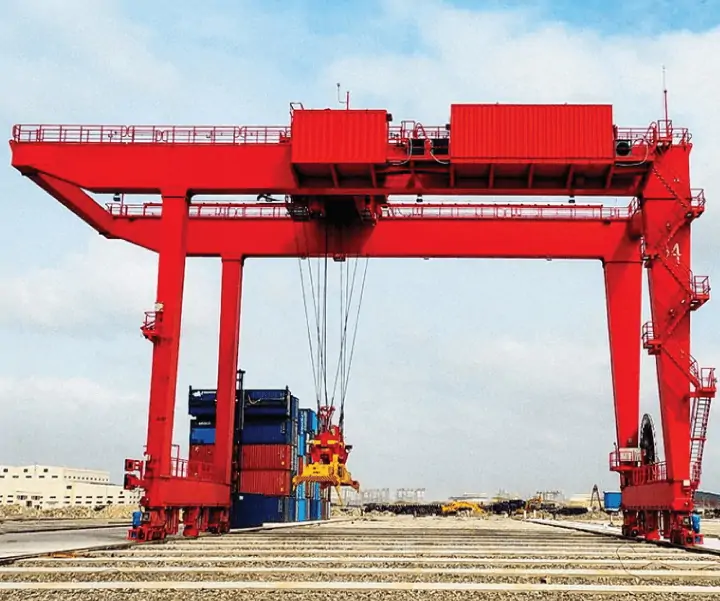




RTG vs RMG Cranes: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages and Disadvantages of RTG Cranes
- Advantages: High mobility, flexible relocation, low initial investment.
- Disadvantages: Rapid tire wear, high maintenance costs, high energy consumption.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RMG Cranes
- Advantages: Stable operation, precise positioning, high degree of automation, low long-term operating costs.
- Disadvantages: Limited mobility range, high initial investment.
Conclusão
RTG vs RMG cranes each have their own advantages. RTGs are suitable for flexible operating scenarios, while RMG cranes are more suitable for high-density automated yards. Nucleon can provide customized design solutions based on your specific operating conditions (such as yard layout, operating intensity, budget, etc.) to ensure optimal loading and unloading efficiency and economy. If you need professional selection advice or customized quotes, please contactar-nos immediately!









