A wire rope electric hoist is a compact lifting device widely used in factories, warehouses, construction sites, and workshops to efficiently and safely handle heavy loads. As usage frequency increases, equipment inevitably experiences wear and tear. Therefore, regular maintenance and inspections are essential to extend service life, ensure operator safety, and reduce downtime costs. Next, we will provide you with a practical wire rope electric hoist inspection checklist, including a safety inspection checklist, maintenance knowledge, and common faults and solutions. Please continue reading.

Wire Rope Electric Hoist Safety Inspection Checklist
| No. | Inspection Item | Inspection Content | Inspection Standard | Compliant? | Inspector |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electrical Control | 1. Is the operating handle intact? 2. Control buttons and contact switches. | 1. Handle casing intact, direction markings clear, no damage. 2. Control buttons and contact switches function correctly. | □ Yes □ No | |
| 2 | Protective Devices | 1. Are limit devices intact and working normally? 2. Is the brake device intact and working normally? 3. Is the anti-dislodgement hook normal? | 1. No kinks, bends, breaks, corrosion, or other defects in the wire rope; rope should be lubricated. 2. Wire rope needs replacement if re-splicing is required, if broken, or if wear reaches 7% of the original diameter. 3. Hook has no cracks, spalling, or other defects; thread section, neck, and surface show no plastic deformation; wear does not exceed 5%; hook opening does not exceed 10% of the original dimension. 4. Hook rotates freely through 360 degrees and swivels freely within 180 degrees from vertical; pulley rotates without jamming or collision. 5. Hook nut locking device is intact, without looseness. 6. Rope guide/reeder is normal; connection points are not loose; no abnormal noise. 7. Wire rope end terminations are securely fixed and reliable, no abnormalities. | □ Yes □ No | |
| 3 | Wire Rope | 1. Are there any cracks or deformations in the pulleys? 2. Is the rail bumper/stop plate intact? 3. Are connections at all locations normal? 4. Is the drum/winding barrel normal? | 1. Is the wire rope intact, without burrs or broken wires? 2. Is the hook specification intact, without wear? 3. Is the wire rope intact? Any corrosion? 4. Does the wire rope usage meet the specified requirements? | □ Yes □ No | |
| 4 | Equipment Main Body | 1. Pulleys are normal, without cracks or deformation; guide rail side guard plates are not deformed. 2. Open gear surfaces are greased; no gear biting/jamming phenomenon. 3. Drum is not deformed, well lubricated; the wire rope is properly secured on the drum. 4. All frame and structural connections are normal; bolts are complete. | 1. No kinks, bends, breaks, corrosion, or other defects in the wire rope; rope should be lubricated. 2. Wire rope needs replacement if re-splicing is required, if broken, or if wear reaches 7% of the original diameter. 3. Hook has no cracks, spalling, or other defects; thread section, neck, and surface show no plastic deformation; wear does not exceed 5%; hook opening does not exceed 10% of the original dimension. 4. Hook rotates freely through 360 degrees and swivels freely within 180 degrees from vertical; pulley rotates without jamming or collision. 5. The hook nut locking device is intact, without looseness. 6. Rope guide/reeder is normal; connection points are not loose; no abnormal noise. 7. Wire rope end terminations are securely fixed and reliable, with no abnormalities. | □ Yes □ No | |
| 5 | Safety Signs | 1. Are safety warning signs complete and intact? | 1. Lifting beam/frame is not deformed; check for cracks or weld failures (Note: This point seems misplaced from equipment body inspection). 2. Wire rope remains intact (Refer to wire rope inspection standards above for checking). 3. Safety warning signs (e.g., load capacity) are complete, clear, and intact. | □ Yes □ No |
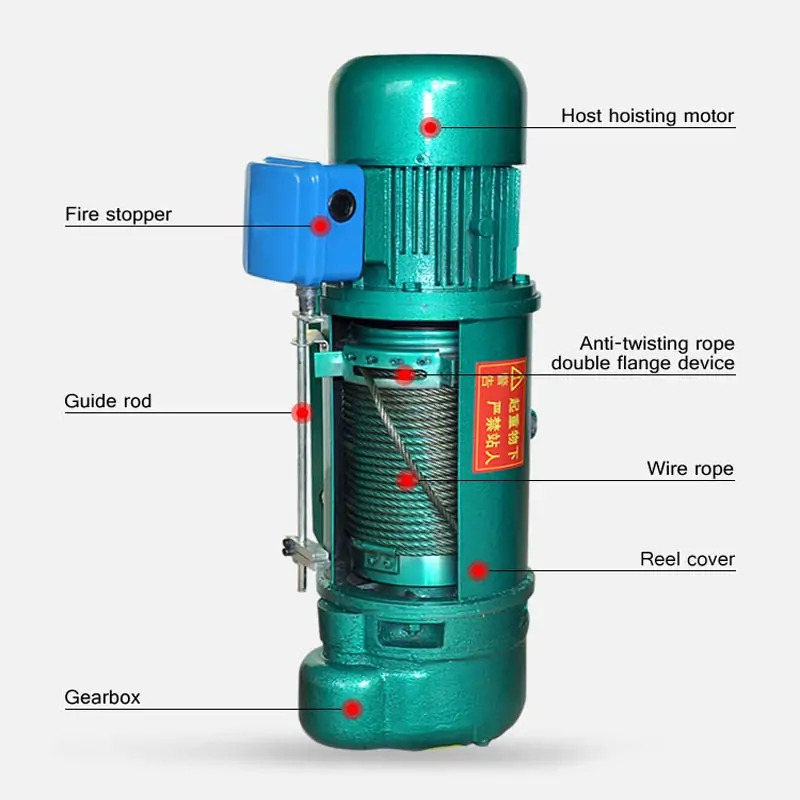


Electric Hoist Maintenance Knowledge:
1. Professional Operation
Maintenance and servicing of electric hoists must be performed by personnel familiar with the equipment's structure and maintenance procedures. Inspection, lubrication, and adjustment of components should be handled by experienced personnel to prevent unauthorized disassembly by non-professionals, thereby avoiding equipment damage or safety hazards.
2. Records and Testing
Each inspection and repair must be documented in detail on a maintenance log for future traceability and management. After completing maintenance, conduct a no-load test run to ensure smooth operation and reliable braking. Only resume normal use after confirming no abnormalities exist.
3. Part Replacement
If damaged or aged components are discovered, replace them promptly. Prioritize genuine manufacturer parts or certified compatible components to guarantee stable performance and safe operation of the electric hoist.
4. Site Cleanup
Debris or oil stains may accumulate during maintenance. Operators must promptly clean the work area to maintain a tidy environment, ensuring both safety and compliance during equipment servicing and subsequent operation.
Adherence to these maintenance guidelines not only extends the service life of electric hoists but also effectively safeguards operator safety and enhances operational reliability.
Common Faults and Solutions for Electric Hoists:
Humming Sound Upon Power-Up
If the starter closes but produces noise, it may indicate poor contact between terminals or motor failure. Inspect the terminals and verify motor functionality.
Inability to Lift Load
If lifting fails despite a functional motor, check for insufficient power supply voltage.
Inaccurate Load Positioning
If the braking travel is excessive, adjust the brake clearance or replace the brake ring. Also check if the spring pressure or friction surfaces are contaminated with oil.
Abnormal Heating of the Electromagnetic Coil
This may indicate a short circuit between coil turns. Perform insulation testing and address promptly.
Contactor Generates Intense Sparks
Sparks result from burnt contact surfaces or frequent high-current closures. Repair or replace the contactor components.
Brake failure
Typically caused by motor shaft or tapered stop ring wear, or improper assembly. Replace damaged components and reassemble correctly to resolve.
Limit switch failure
When the load reaches the end position but fails to limit, it is often due to an incorrect power phase sequence or loose limit stop blocks. Correct power phase sequence and secure stop blocks.
Conclusão
Each inspection should strictly record the inspection time, inspector, inspection results,any problems and rectifications in accordance with regulations,and the inspection records should be properly preserved. Minor faults discovered during the inspection should be rectified immediately. If the problem is serious,the equipment should be shut down for rectification and not reactivated until it passes the inspection. Only by strictly following the above inspection items can the failure rate of electric hoists be effectively reduced,the service life of the equipment be extended,and the safety of personnel be guaranteed.